In my Bachelor Thesis my teammates and I researched the situation in overcrowded emergency rooms in Germany and developed four interventions aiming to relieve the affected medical personal and patients.

Can Design Relieve Overcrowded Emergency Rooms in Germany?
Emergency Rooms in Germany are overcrowded resulting in overworked medical staff and long waiting times for patients. for many years, legal and regulatory reforms have been called for. Until they come and take effect, we wanted to explore the possibilities of a human-centered design approach to relieving the situation in German emergency rooms.
Combining Research Methods to understand the Problem.
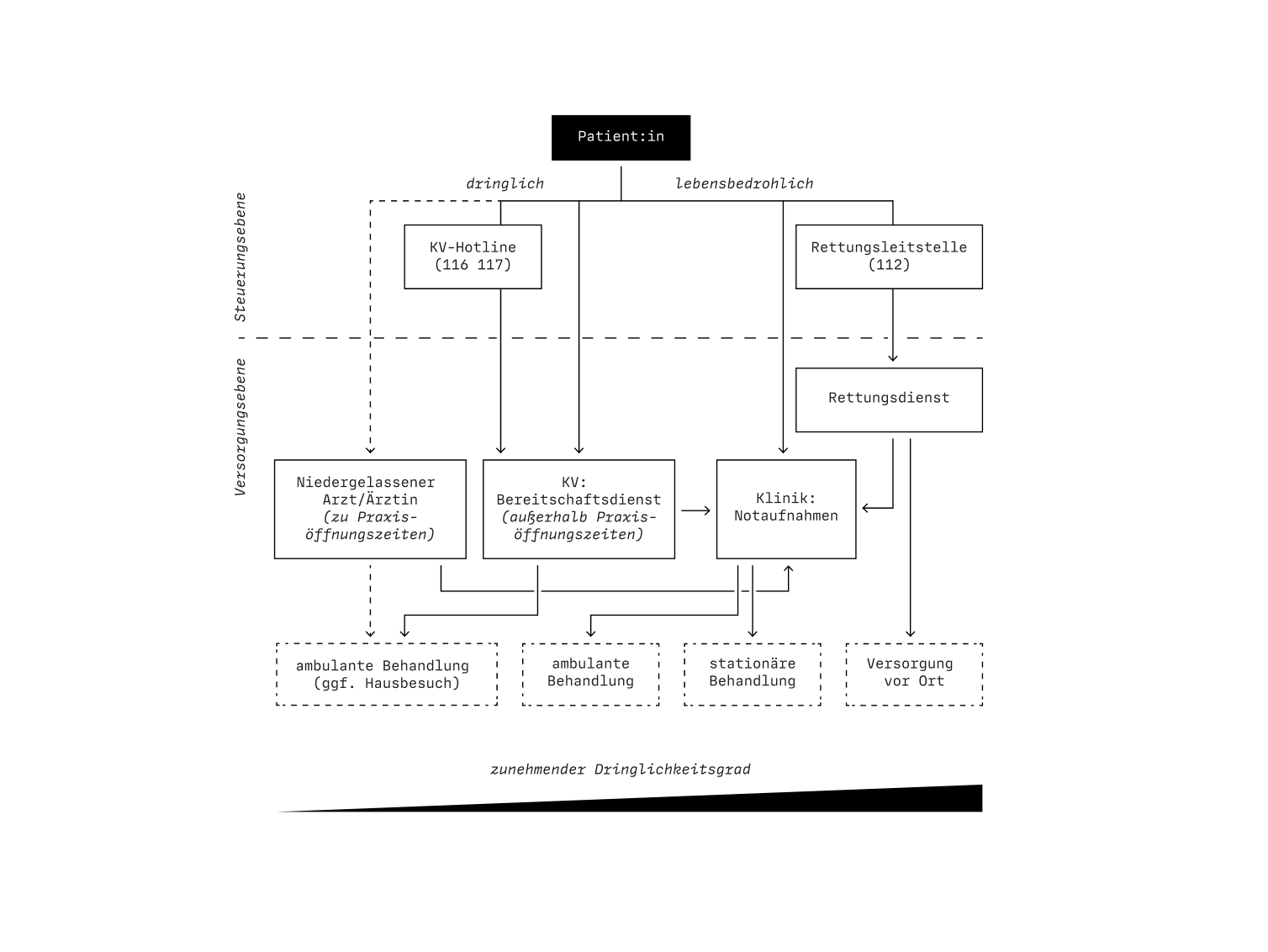
To understand the underlying issues for overcrowded ERs in Germany we conducted a broad general research of the german emergency medical care system and the operation of ERs in specific. We combined primary and secondary research methods, including literature research, qualitative interviews with medical staff, quantitative survey of patients and on-site observations in the ER.
Field Research

Qualitative Interviews

Quantitative Survey

Litearture Research
Three Key Insights from Analyzing the Causes and Consequences of Overcrowded Emergency Rooms.
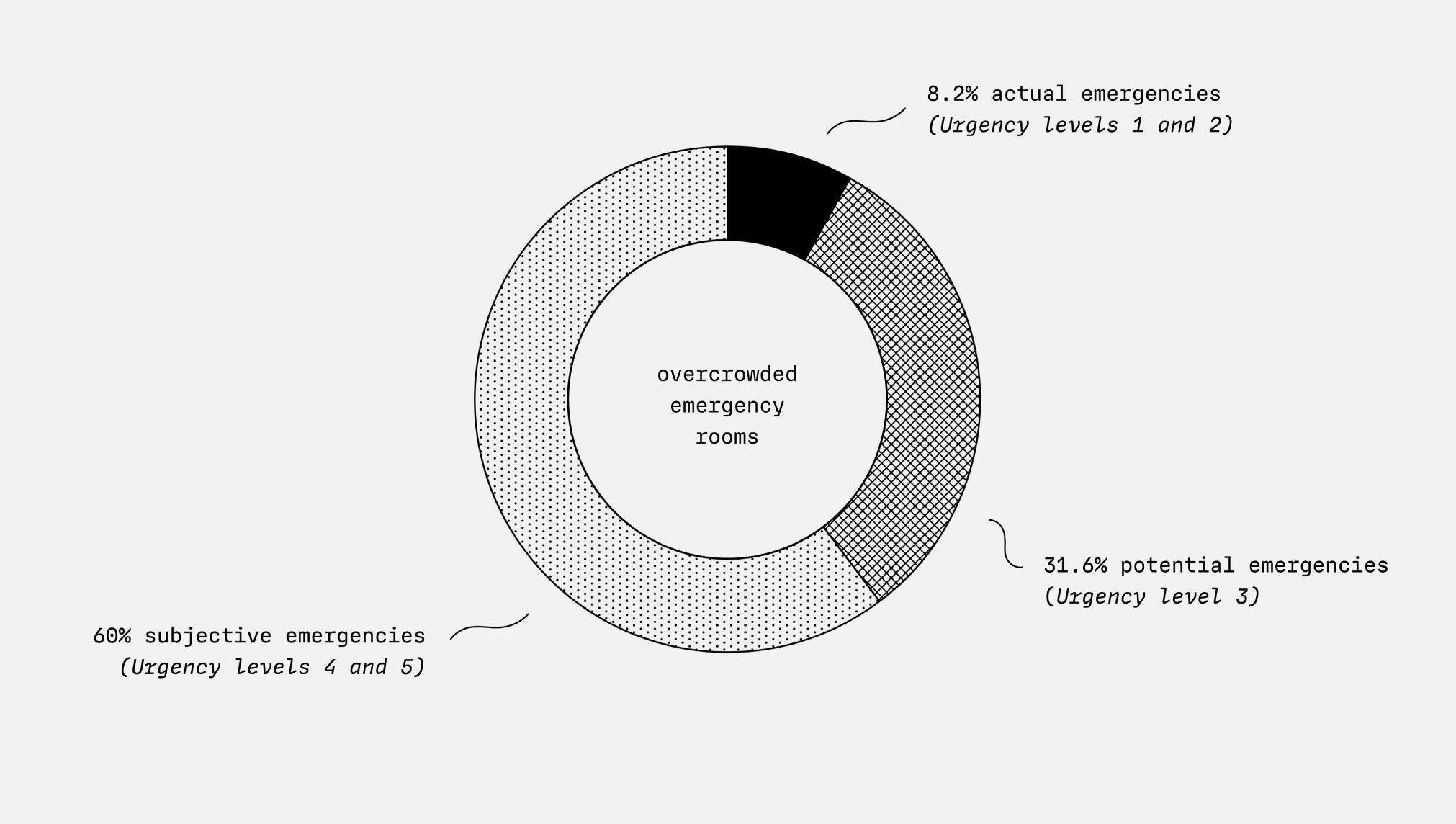
Too Many Subjective Emergencies.
Overcrowded emergency departments are not synonymous with too many emergencies: Approximately 60% of patients are not medical emergencies. They subjectively see themselves as being in an emergency situation, but could have visited another medical point of contact.
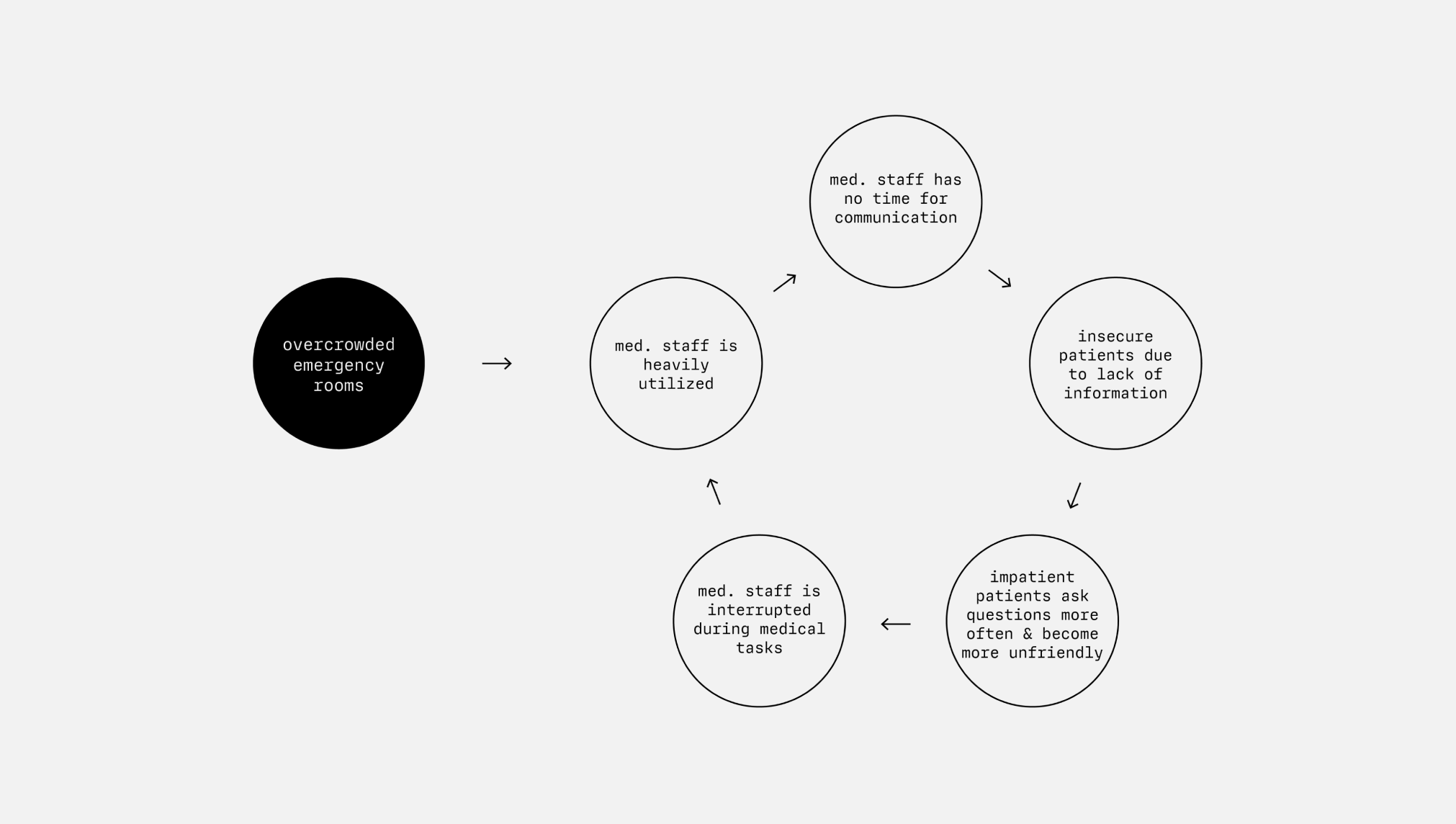
Downward Spiral in Communication.
In overcrowded emergency departments, medical staff are working at full capacity. They focus on the medical care of patients. This leaves no time for detailed communication with patients, which leads to uncertainty and a negative spiral.
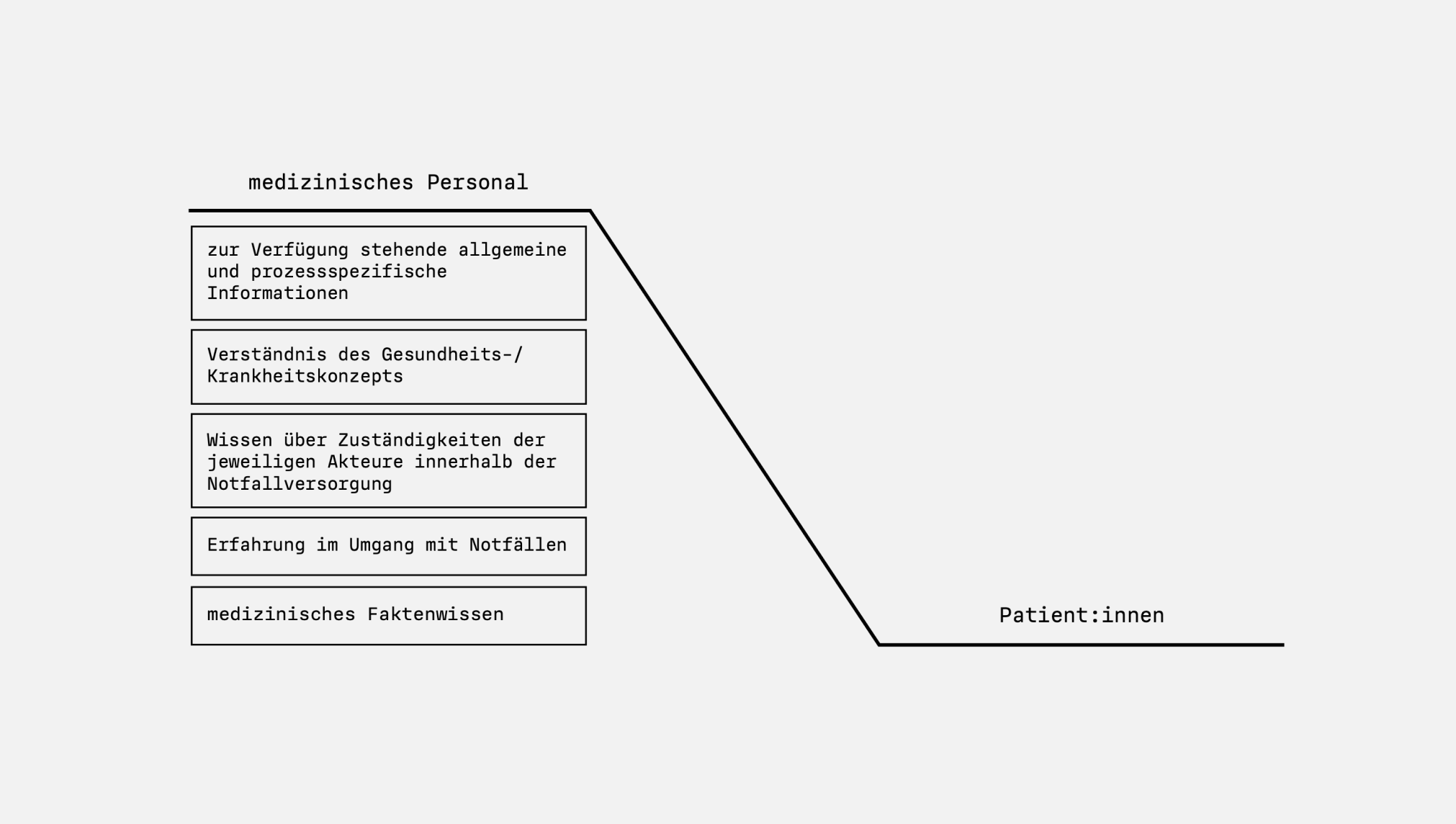
Information and Knowledge Gap.
The medical staff and patients in the emergency department have different levels of knowledge, information and experience. This often results in patients feeling insecure and a subjective misjudgment of their own medical situation.
Choosing Two Design Frames for Developing our Interventions.
We combined the findings from research and analysis into a bigger picture. This allowed us to look at the causes and consequences of overcrowded ERs holistically – both from the perspectives of the medical staff and the patients. Within this problem space we identified two Design Frames in which we wanted to start developing our interventions.
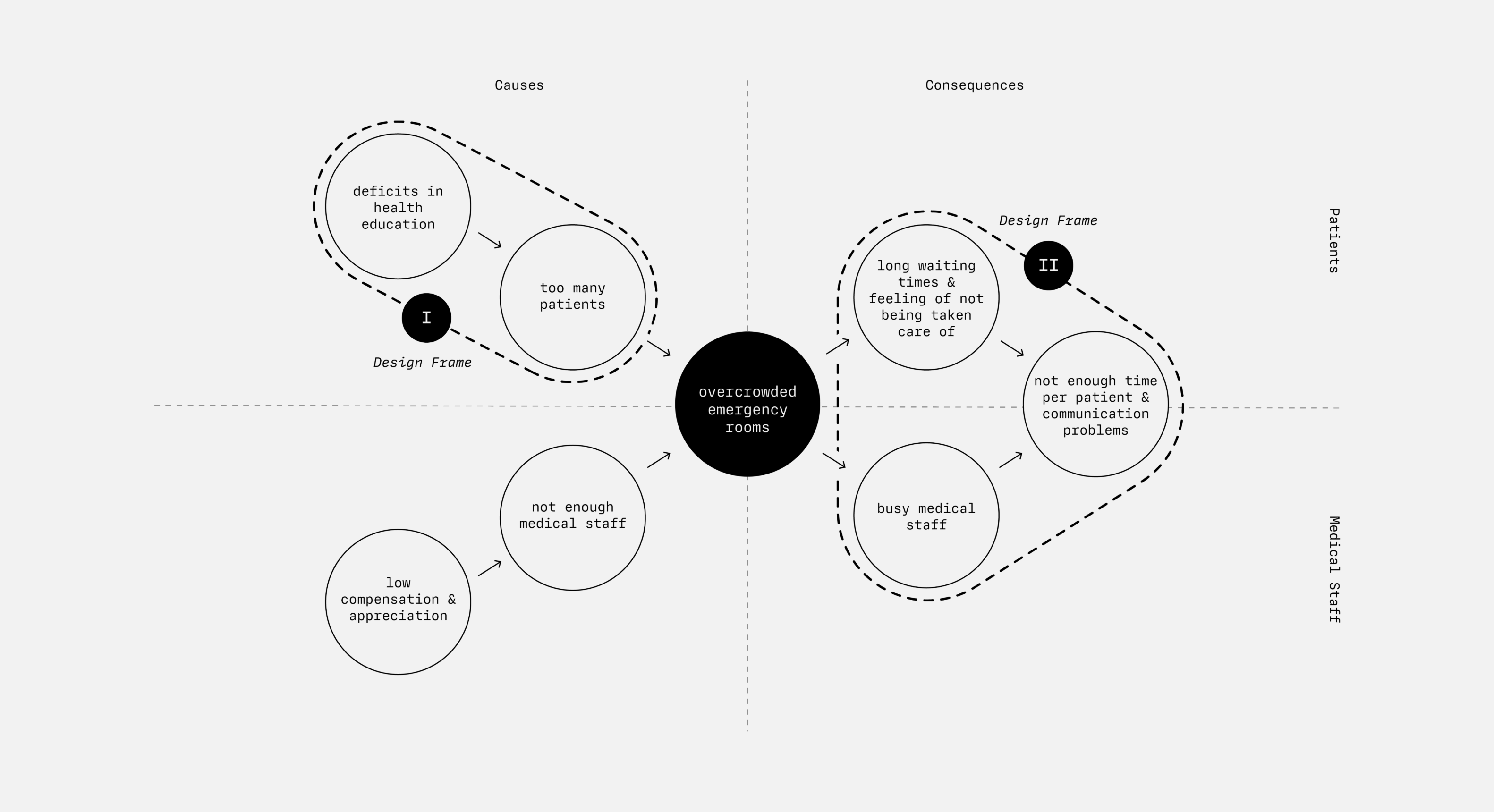
DESIGN FRAME I
Address the Deficits in Patient Health Education.
Regarding the causes, we would like to address the deficits in patient health education: How can we manage to refer patients in a (subjective) emergency situation to the appropriate point of contact for their concerns?
DESIGN FRAME II
Mediate between Patients and Medical Staff.
On the side of the consequences, we want to relieve the situation in the ER through creative moderation between patients and medical staff: How do we manage to inform patients in such a way that their uncertainties are taken away and they develop an understanding of the current situation (waiting times, processes, ...)?
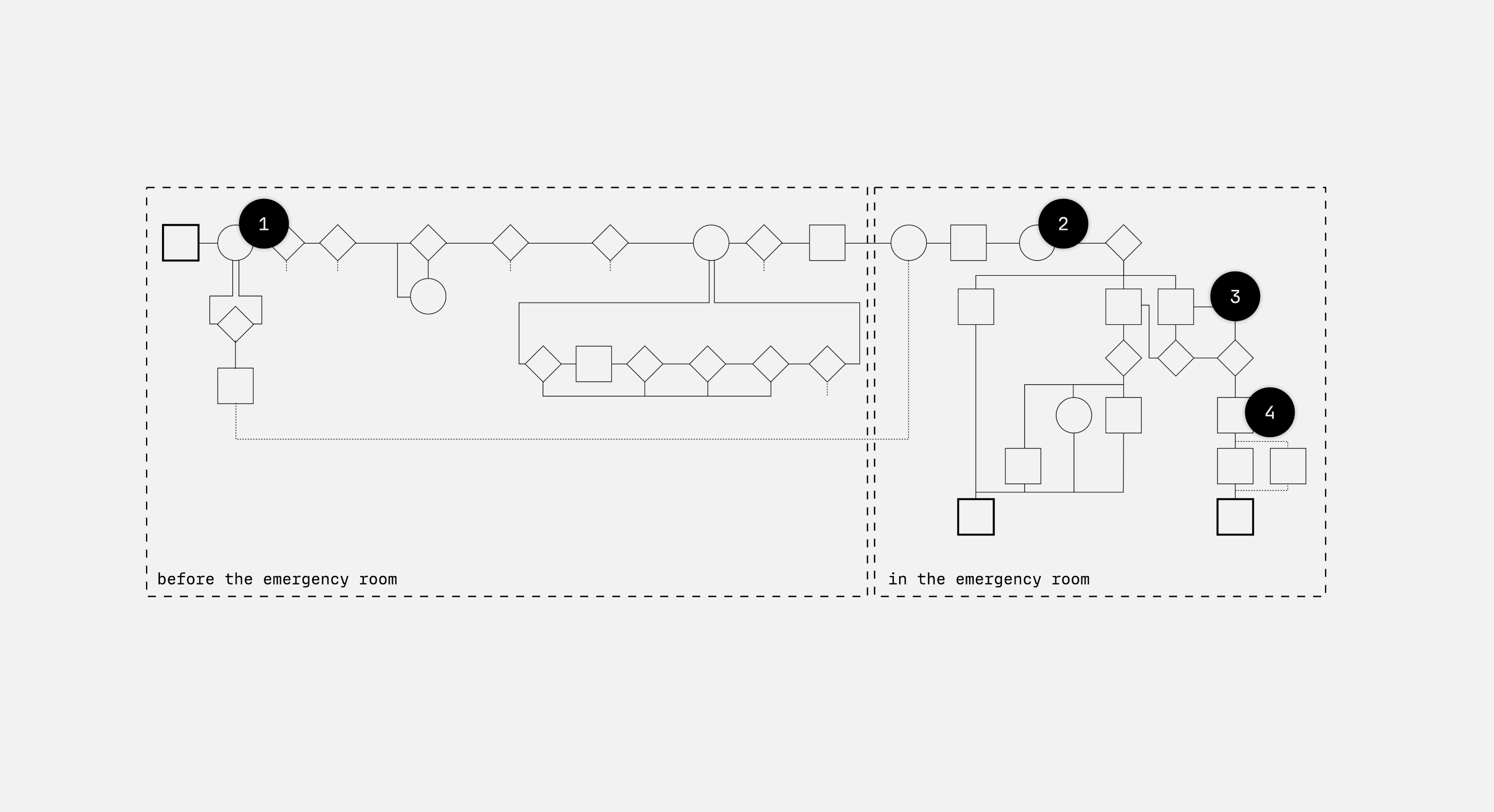
Four Design Interventions Placed Along the Patients Journey in an Emergency.
We propose four design interventions along the patient journey in a medical emergency situation. Starting with the patient recognizing a symptom, deciding to go to the emergency room, being treated and finally discharged from the ER.
INTERVENTION 1
Situational Decision Aid to Guide Patients to the Right Medical Contact Point.
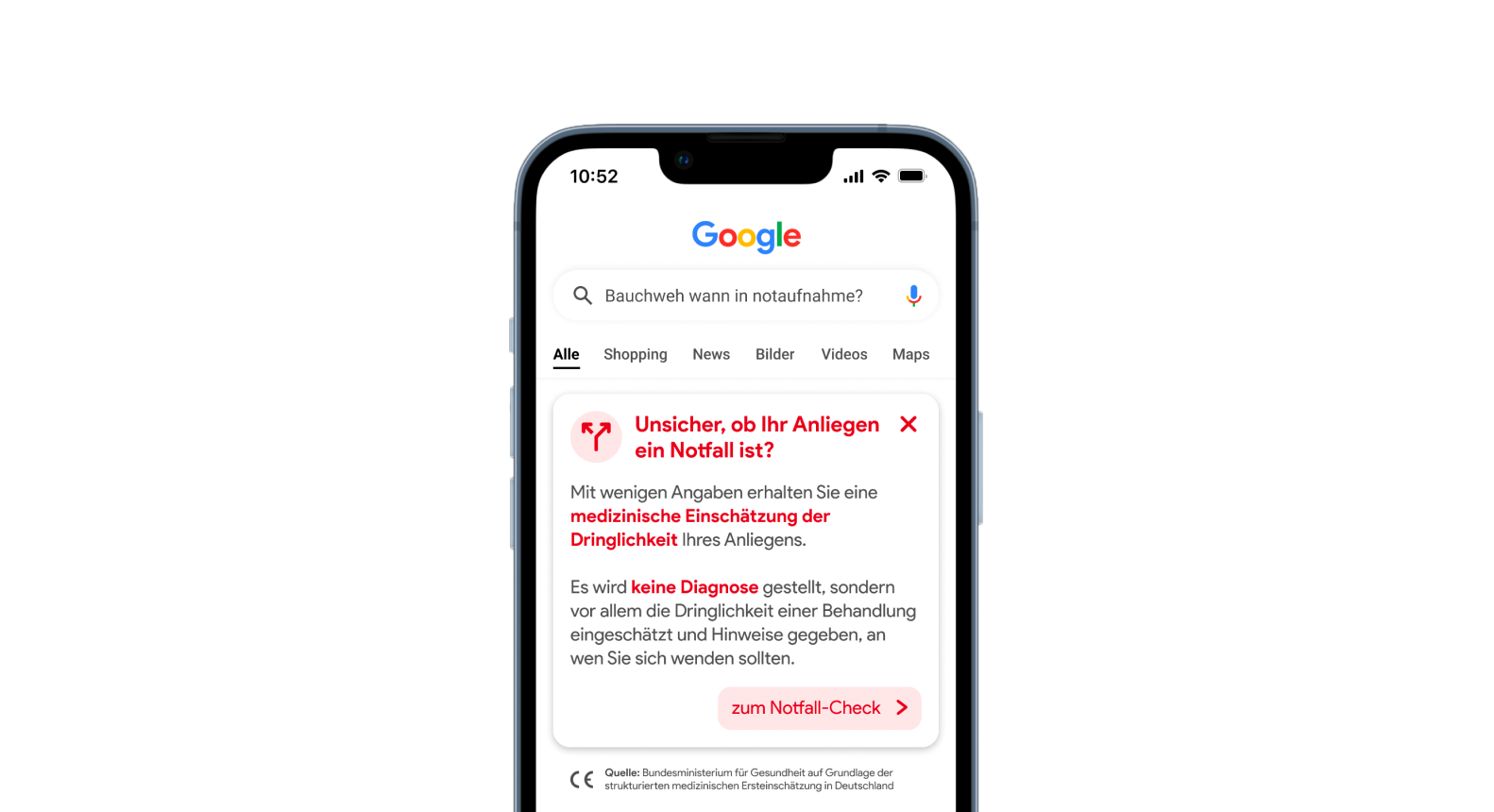
STATUS QUO
The Emergency Room as the Go-To Address.
In a situation of medical uncertainty the selection of the contact point happens often very quickly and according to subjective feelings is made in a very short time. The decision is often made in favor of the emergency room. Alternative medical points of contact and services such as the 116 117 telephone patient service are largely unknown among the public. Due to their uncertainty, patients have a need for fast and reliable information to be able to assess the urgency of their concerns.
CONCEPT
Google Knowledge Panel with Context Sensitive Information.
Especially in medically ambiguous situations
search engines are an easily accessible way for many people to obtain information. Instead of
well-founded medical knowledge that provides clarity, the user is presented with a flood of information.
This leads to even more uncertainty.
With a context-based and visually highlighted Google Knowledge Panel, we want to address and mentally
reach-out to patients in the decision-making process. The aim is to quickly redirect them to the
medically sound online urgency assessment of the medical on-call service (116 117).
INTERVENTION 2
Transparent Triage to Make the Initial Medical Assessment and Order of Treatment Comprehensible.
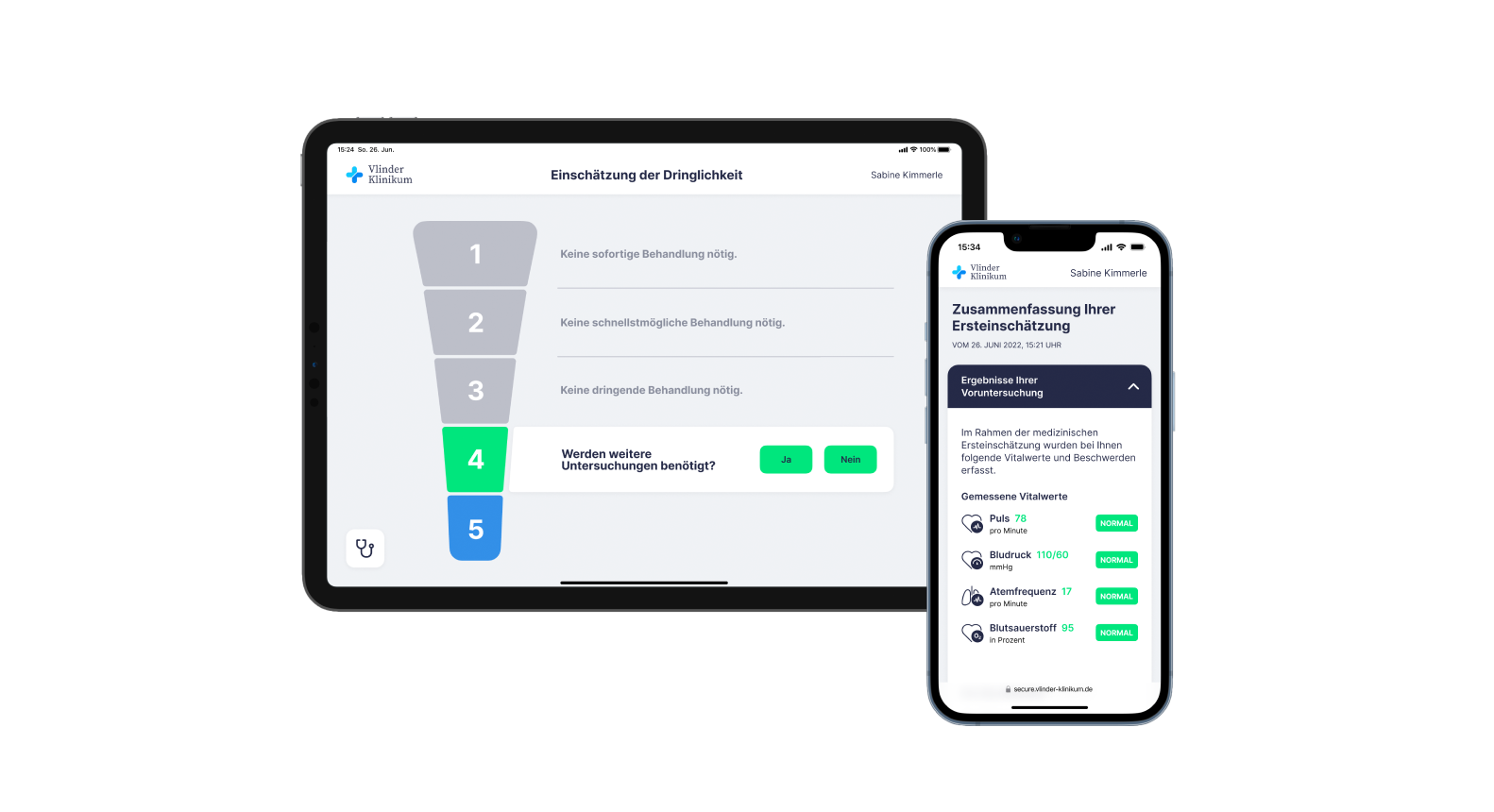
STATUS QUO
Uncertainty due to Lack of Explanation.
All patients in the emergency department undergo a standardized initial medical assessment. The urgency of the case is determined and a order of treatment is established. Both the initial assessment and the order of treatment are not communicated transparently to patients due to time constraints. This leads to a lack of understanding and frustration. Incoming patients want their concerns and uncertainty to be acknowledged and to be treated fairly.
CONCEPT
Tablet Application to Explain Triage to Patients.
By providing a transparent urgency assessment, we aim to reduce patient uncertainty and make the
underlying principle of determining the treatment order comprehensible. At the same time, by presenting
alternatives to waiting, we create a decision-making situation that puts patients in an active role.
A tablet application serves as a tool for nursing staff to explain and visually justify the concept of
urgency assessment. The results of the initial assessment are summarized for patients and supporting
information is provided if the patient decides to discharge themselves.
INTERVENTION 3
Transparency in the Waiting Area to Make Waiting Times Comprehensible and Create Realistic Expectations.
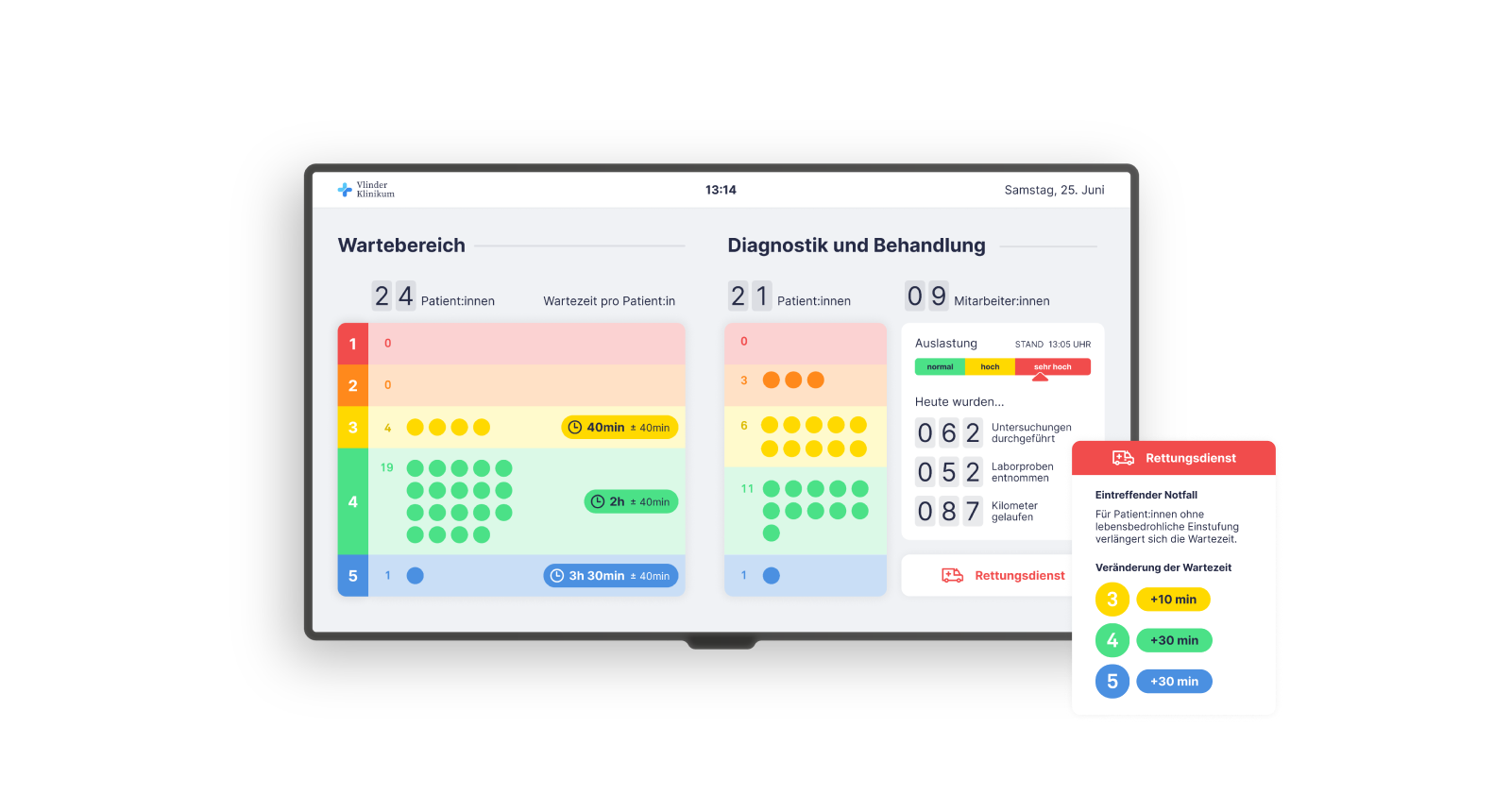
STATUS QUO
Confusion due to Lack of Explanation.
People waiting do not know the practical meaning of their urgency level and cannot put their case in relation to others. In addition, it is not clear in the waiting room what is going on in the treatment area of the emergency room and what the approximate waiting time is. Patients want to be able to comprehend the waiting times that occur, while medical staff want reasonable expectations and mutual understanding.
CONCEPT
Monitor with Overview of the Emergency Room’s Capacity.
Through transparency and honest communication, we want to make the processes happening in the background
visible, thereby creating an understanding of the current situation and realistic expectations.
A monitor that can be viewed by everyone in the waiting area displays constantly updated, anonymized
information on capacity utilization and processes. This “window into the emergency room” and the
knowledge of their urgency level allows patients to put themselves and their needs in relation to each
other.
INTERVENTION 4
Accompanying Information During Treatment to Make Hidden Processes and Waiting Times Comprehensible.
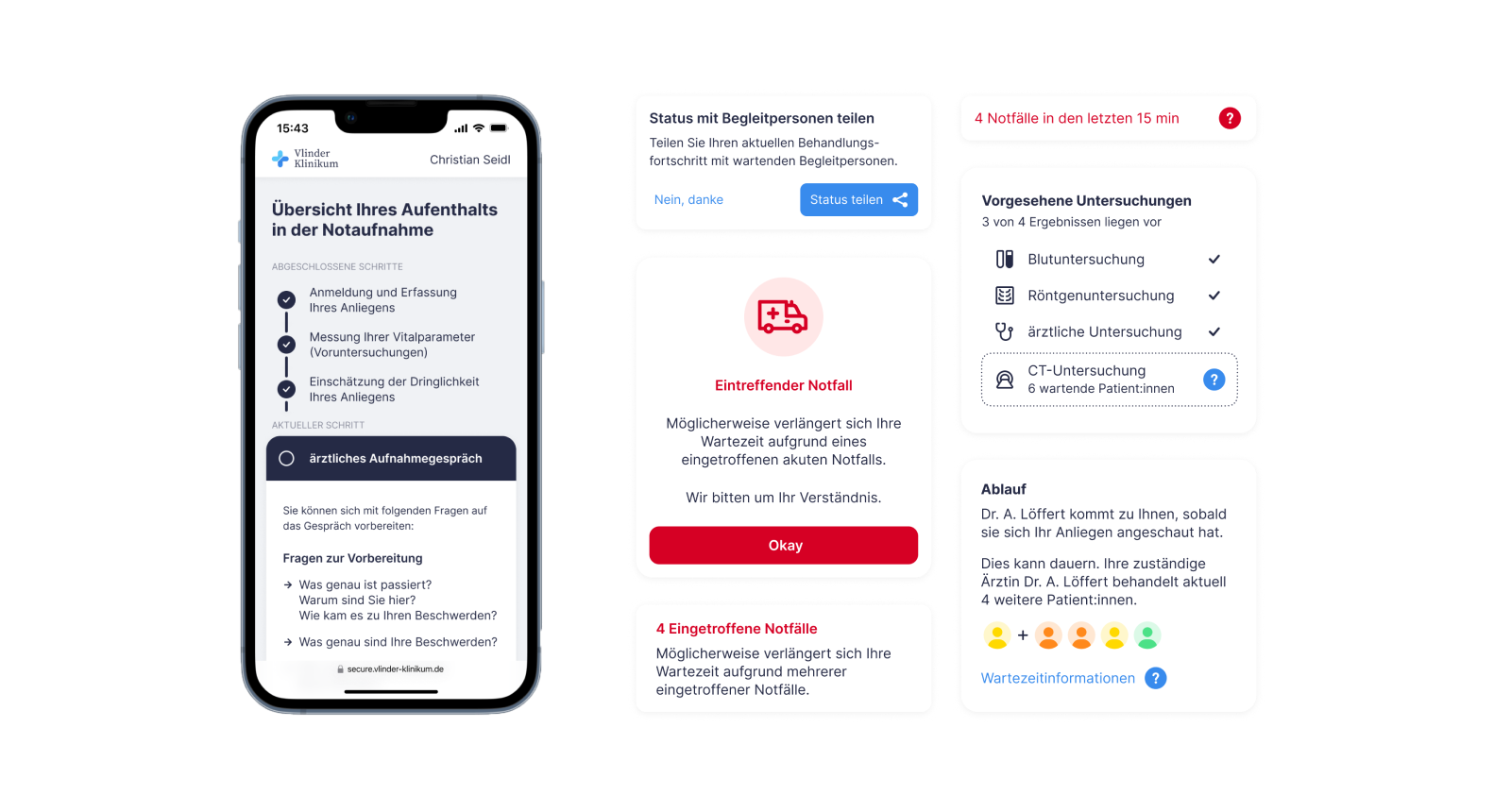
STATUS QUO
Hidden Processes Create Impression of Standstill.
PIn the area of diagnostics and treatment, many processes run simultaneously and medical assessments take place in the background. Medical staff make decisions quickly and according to the situation. There is not enough time to explain upcoming measures to patients in detail. As a result, many work steps remain invisible to patients and their waiting companions and they have the impression that no progress is being made. Patients want to understand what is happening to them and be informed about upcoming steps and how long they will take.
CONCEPT
Web App With Personalized Live Information During Treatment.
We want to prepare patients openly and honestly for upcoming steps or measures as well as waiting times.
This should minimize uncertainties, ambiguities and the resulting questions and create realistic
expectations among patients.
A web app that can be accessed in the emergency room gives patients access to individual, accompanying
information along their treatment journey. This allows them to follow a clear structure and mentally
prepare for the steps ahead. The information can also be shared with a companion in a less detailed
version.
